Flared End Section Vs Headwall
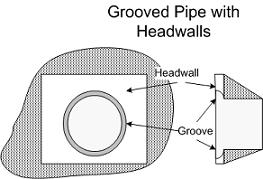
Flared end section vs headwall Calculations shall be submitted with plan review. Flared, improved, or tapered inlets indicate a special entrance condition which decreases the amount of energy needed to pass the flow through the inlet and thus increases the capacity of culverts at the inlet. Beveled edges, 33.7 or 45 degree bevels: Approach velocities are between six (6) and ten (10) feet per second. The concrete flared end sections are. End sections are manufactured in accordance with applicable portions of astm specification c506.click here for information on trash guards. 36 key rcp standard indices. The end of culverts can be treated with a variety of options depending on the situation. A longitudinal bar is required for cross drainage end sections when the span is greater than 30 inches. Tie bolt holes are provided for the installation of tie bolts between the flared end section and the adjacent pipe.

Jensen Precast - Tucson - Reinforced Concrete Pipe - Concrete Pipe
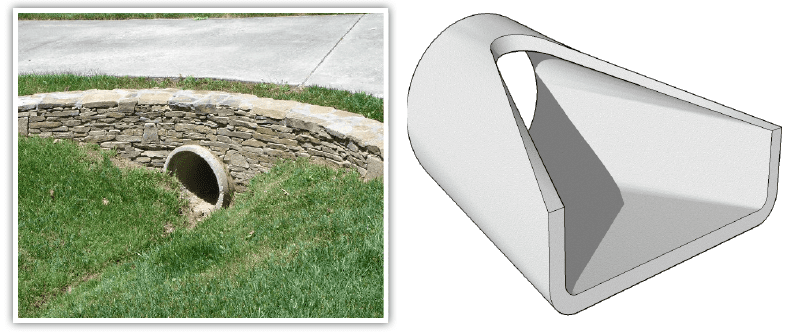
End section conformed to fill slope: Riprap or geotextile, for outlet protection materials Under inlet control, standard flared end sections perform much better than mitered pipes, slightly better than headwalls with sharp inlet edges, and slightly worse than headwalls with grooved or rounded inlet edges. They are used to keep the earth away from pipe openings and provide support for bridges and roadways. Culvert flared end sections have many advantages. Lets you define the slope correction factor to be used in inlet control calculations.

Flared end section vs headwall. Headwalls (left image above) can be used as a retaining measure while adding visual interest in areas of high visibility. The user may model projected or mitered end treatments on a culvert link with a connection to a cross section or outfall node. End section conforming to fill slope: Identify location of items by plus station and station offset distance. Cost less than other types of concrete headwalls. Ample right of way or easement is available. Headwalls and endwalls support the road and protect the ends of the pipe. Only a conduit link can be used to model a culvert. Headwalls, wingwalls, drainage inlets, flared end sections, inlet and outlet structures, shown and labeled. • existing groundline profile (shown as dashed line) and finished grade (shown as solid line). Flared end section (fes) headwall concept. Coarse aggregate • section 902: A conduit that is declared to be a culvert link may have a headwall node at either end. Higher than the top of the drain pipe outlet section: Projecting form fill (no headwall) 0.9: Flared end sections fit to either cmp or concrete are also considered straight inlets. Completely wrapped in nonwoven opening. Headwall or headwall with square edge wingwalls: Standard flared end section for metal pipe culverts, or geotextile, for inlet protection diversion dike height: =user name plot scale = =. Block of aggregate shall be ca11 coarse aggregate placed over drain 12 x 12 x 6 block of ca5, ca7, or. Soffit soffit refers to the inside top of the culvert. Approach velocities are low (below six (6) feet per second).
Pipe coupling and joint details; Location manholes or structures shall be installed at each deflection of line or grade. • all flow line elevations. Corrugated metal pipe or pipe arch : Keep the culvert opening free from grass and weeds. For single, twin, or triplebarrels; Higher than the top of the drain pipe island over inlet height: Flared end sections provide a less expensive option in areas of lower visibility. Perimeter of fabric nonwoven geotextile fabric centered provide a double layer of 12 x 12 geotextile fabric. Reduce erosion at ends of culvert. Increase stability with greater bearing area. Properly constructed headwalls and endwalls improve pipe efficiency while reducing erosion around pipe installations. The wings of flared walls should be located with respect to the direction of the The sloping wing walls coincide with the embankment slope. Flared end headwalls are a type of retaining wall, commonly found near waterways. Mitered (beveled to conform to fill slope) 0.7: Metal and plastic flared end sections: Safety and longitudinal bars are not required on 30 inches and. Flared end section (fes) headwall concept. Precast concrete flared end headwalls offer convenience, time. If the conduit is a culvert, define the nomograph form to use in culvert calculations. Use additional longitudinal bars if spacing exceeds 30 inches on larger end sections.
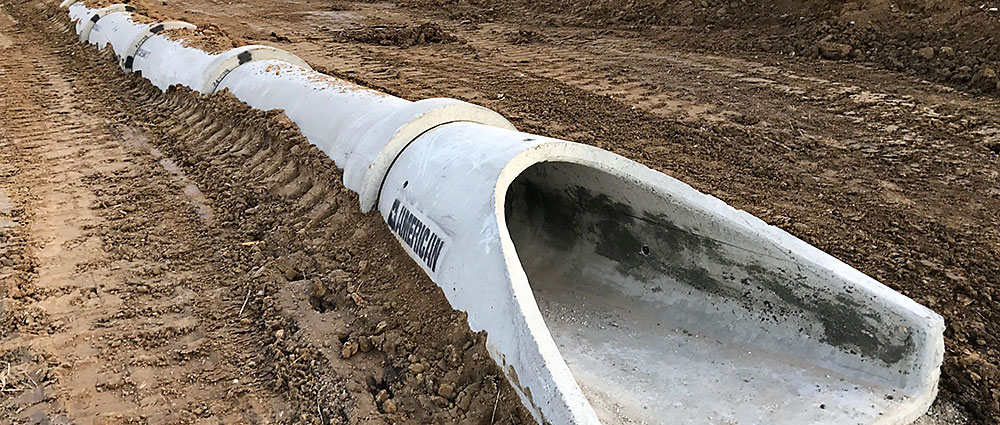

Flared Ends Structural Prestressed Precast Concrete
Hy8inlet Configurations - Xms Wiki

Headwallsend Treatments - Foley Products
Culverts And Piping - Standards - Great Rivers Greenway
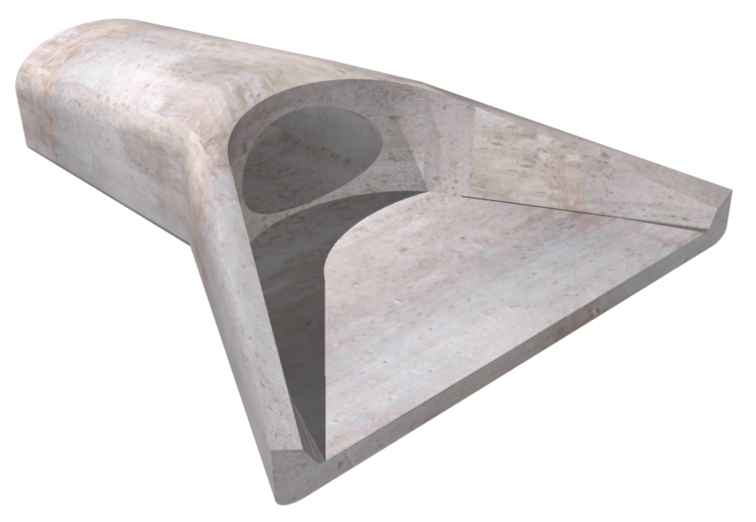

Pipe-elliptical Flared End Section Oldcastle Infrastructure
0 Response to "Flared End Section Vs Headwall"
Post a Comment